 CH3Br emissions calculated from inverse model of baseline measurements (Fig 2 in paper)
CH3Br emissions calculated from inverse model of baseline measurements (Fig 2 in paper)Abstract
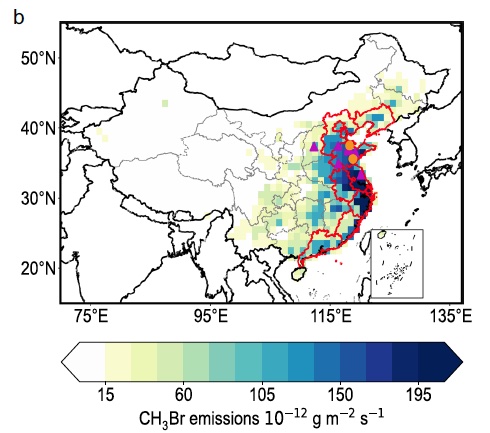
Methyl bromide (CH3Br) is an important ozone-depleting substance whose use is regulated under the Montreal Protocol. Quantifying emissions on the national scale is required to assess compliance with the Montreal Protocol and thereby ensure the timely recovery of the ozone layer. However, the spatial-temporal patterns of China’s national CH3Br emissions remain unclear. Here we estimate the national emissions of CH3Br in China during 2011−2020 using atmospheric observations at 10 sites across China combined with an inversion technique (top-down) and compare those with an updated inventory of identified emission sources (bottom-up). Measured CH3Br mole fractions are enhanced well above the background mole fractions, especially at sites in eastern China. Topdown emission estimates exceed bottom-up estimates by 5.5 ± 1.4 gigagrams per year, with the largest fraction (60%) of observationally derived CH3Br emissions arising from underestimated or unidentified emissions sources. This study shows the potential impacts of the unaccounted emissions on stratospheric ozone depletion, with implications for the Montreal Protocol.